With the continuous advancement of photovoltaic power generation technology and the continuous reduction of costs, photovoltaic power generation has become one of the mainstream renewable energy sources. Many countries and regions have introduced a series of policies to support the development of the photovoltaic industry.
In addition to solar inverter like 2000w inverter or 3000w inverter, photovoltaic glass is also an important component of the photovoltaic industry, and it is naturally attracting much attention. Photovoltaic glass refers to the glass used on solar photovoltaic modules, which has the important value of protecting cells and transmitting light.
This article will give you a detailed introduction to what photovoltaic glass is, what types there are, the quality requirements of solar panel glass, and the photovoltaic glass faults, etc.
Main content:
1. What is photovoltaic glass
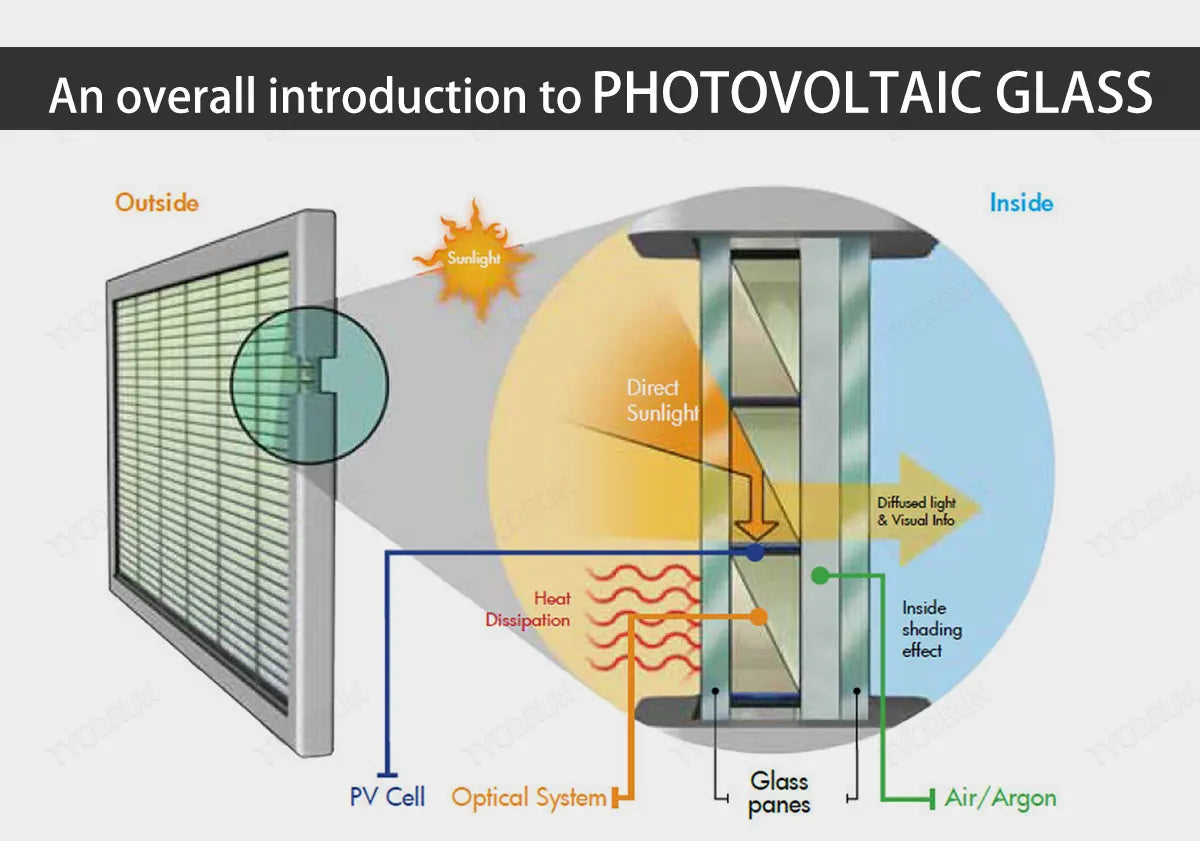
Photovoltaic glass refers to the encapsulating glass used in solar photovoltaic modules, it is generally used on the upper surface of photovoltaic modules. Double-glass modules require photovoltaic glass on both sides. Photovoltaic glass is generally low-iron tempered glass or semi-tempered glass. It must have a certain mechanical strength.
It is generally required to withstand wind pressure of more than 2400Pa and snow pressure of more than 5400Pa. It plays a role in protecting the internal battery. It also requires high light transmittance and it should have a higher reflectivity for infrared light greater than 1200nm to improve solar panel efficiency.

2. Classification of photovoltaic glass
① Low iron tempered glass
The mainstream products of crystalline silicon photovoltaic modules all use low-iron (i.e. ultra-white) tempered rolled glass. Because the iron content is very low and there are few bubbles, the light transmittance can generally exceed 93.8%, and it has a high sensitivity to infrared light greater than 1200nm, thus improving the efficiency of components. In addition, the thickness requirement is 3.2mm, which makes it can enhance the impact resistance of components and act as a seal for components.
Most manufacturers coat the surface of tempered photovoltaic glass with an anti-reflection coating. The purpose is to increase the power generation of the module by increasing the transmittance of visible light when the conversion efficiency of the module is fixed.
The principle of glass anti-reflection coating is to form a porous silicon oxide film on the surface of the glass, and use the volume ratio of the voids to adjust the effective refractive index of the film to about 1.22, thereby achieving the purpose of anti-reflection at a wide spectrum and large angle. Anti-reflection coating can increase the efficiency of photovoltaic modules by about 2.5%. At the same time, the anti-reflection coating also plays a certain self-cleaning role.
As major module manufacturers have launched double-glass photovoltaic module products, double-glass modules have attracted increasing attention from industry insiders. The photovoltaic glass used on the front of double-glass products is generally low-iron tempered rolled glass. Some products also use low-iron tempered float glass in order to pursue higher light transmittance.

② Semi-tempered glass
Because the cost of semi-tempered glass is lower than that of tempered glass, semi-tempered photovoltaic glass is often used on the back of double-glass products. Semi-tempered photovoltaic glass is also called heat-reinforced glass. It is a type between ordinary flat glass and tempered glass.
It has some advantages of tempered glass, such as higher strength than ordinary flat glass, which is twice that of ordinary flat glass. At the same time, it avoids the unsatisfactory weaknesses of tempered glass such as poor flatness, easy self-explosion, and overall shattering once damaged.
When semi-tempered photovoltaic glass is damaged, it will crack radially along the crack source, and there is generally no tangential crack expansion, so it can generally remain intact after damage.
3. Photovoltaic glass tempering process
Tempered photovoltaic glass is a secondary processing product of flat glass. Tempered glass can be divided into physical tempering method and chemical tempering method according to the processing technology.
① Physically tempered glass
Also known as quenching tempered glass (heating the metal workpiece to a certain appropriate temperature and maintaining it for a period of time, and then immersing it in a quenching medium to rapidly cool it). It is obtained by first cutting ordinary annealed glass into the required size, then heating it to about 700℃ close to the softening point, and then cooling it quickly and evenly.
Usually the 5-6mm glass is heated at 700℃ for about 240 seconds and cooled for 150 seconds. 8-10mm glass is heated at a high temperature of 700℃ for about 500 seconds and cooled for about 300 seconds. In short, according to the thickness of the glass, the heating and cooling times are also different.
After tempering, uniform compressive stress is formed on the surface of the glass, while tensile stress is formed inside. It is in a stress state of internal tension and external compression, which improves the bending and impact strength of the glass. Its strength is about four times that of ordinary annealed glass.
Tempered photovoltaic glass that has been tempered cannot be subjected to any cutting, grinding or other processing or be damaged, otherwise it will break due to destroying the balance of uniform compressive stress. Once partial damage occurs, stress will be released and the photovoltaic glass will be broken into countless small pieces. These small pieces have no sharp edges and are not easy to hurt people.

② Chemically tempered glass
The strength of photovoltaic glass is improved by changing the chemical composition of the glass surface, which is generally manufactured using a low-temperature ion exchange process. The so-called low temperature refers to the range where the exchange temperature is not higher than the glass transition temperature, which is the temperature range above the transition temperature and below the softening point of the high-temperature ion exchange process.
The principle of the low-temperature ion exchange process is to exchange ions with a smaller radius in the surface layer of the photovoltaic glass with ions with a larger radius in the solution in an alkali salt solution at about 400℃, such as lithium ions in the glass and potassium or sodium ions in the solution. The difference in volume of alkali ions is utilised to create embedded extrusion stresses in the glass surface.
The number of large ions squeezed into the photovoltaic glass surface is proportional to the surface compressive stress, so the number of ion exchanges and the depth of the exchanged surface are key indicators of the enhancement effect.
The stress distribution of ion exchange tempered glass is different from that of physically tempered glass. The compressive stress thickness of the surface layer of the former is small, and the internal tensile stress that balances it is not large. This is why the internal tensile stress layer of chemical tempered glass is not like physical tempering when it reaches damage and breaks into small pieces.
Since the ion exchange layer is thin, the chemically tempered glass method has a significant effect on strengthening thin glass, but has less obvious effect on thick glass. It is especially suitable for strengthening glass with a thickness of 2 to 4 mm.

4. Requirements for solar panel glass
Solar panel glazing requirements are one of the key factors in ensuring the performance, durability and safety of the solar module. Here are some common solar panel glass requirements:
- Light transmission: The solar panel glass must have a high degree of light transmission to ensure that sunlight can penetrate and reach the off grid solar batteries without any problem, thus enabling efficient photovoltaic conversion.
- Ultraviolet (UV) resistance and UV care: Solar panel glass should have good UV resistance properties to prevent damage to the solar cell module from UV radiation. In addition, some solar glass uses special coatings to provide additional UV protection.
- Anti-reflective coating: Some solar panel glass is coated with an anti-reflective coating to reduce reflective losses and increase the absorption of light, thereby improving efficiency for the home solar power system.
- Hardness and scratch resistance: solar panel glass needs to be hard enough to prevent scratching or abrasion. This helps maintain the appearance and preserve the transparency of the glass.
- Chemical resistance: Solar panel glass should be chemically resistant to atmospheric pollutants, rain, corrosion, etc. to ensure consistent performance over time.
- Anti-reflective glass: Some solar modules use anti-reflective glass to reduce reflection losses and improve light absorption.
- Impact resistance: Solar panel glass needs to be impact resistant to prevent glass breakage or damage, especially in stormy or hail weather conditions.
- Insulation: Solar panel glass should have good electrical insulation properties to ensure the safe operation of the battery module and prevent current leakage.

5. Common faults of photovoltaic glass
- Burst by itself
Generally divided into three reasons:
① Burst by itself because of visible defects in the glass, such as stones, sand, bubbles, inclusions, gaps, scratches, edge damage, etc.;
② Tempered glass bursts by itself because of nickel sulfide (NIS) impurities and heterogeneous particles in the glass;
③ Uneven stress distribution in the glass caused by uneven tempering leads to glass bursting.
- Burst due to external reasons
① Transportation and logistics accidents;
② For rough construction at the project site, generally component factories will conduct training for project installation and handling;
③ The project design is improper and the spacing is small. When the temperature is high, the components squeeze each other, causing bursting;
④ Improper cleaning and failure to follow the requirements of the component installation manual. High-temperature components may encounter cold water and cause the glass to burst.
Related posts: global top 10 best solar inverter brands, install solar panel, how to clean solar panel