
Main content:
With the growing global focus and demand for clean energy, the photovoltaic industry is experiencing unprecedented development. As a key component of PV modules, photovoltaic backsheet materials play a key role in improving photoelectric conversion efficiency, reducing costs, and addressing environmental challenges.
However, despite the broad market prospects of distributed pv system, competition within the industry is also becoming increasingly fierce, especially in terms of the variety and quality of photovoltaic backsheet materials.
1. What is photovoltaic backsheet
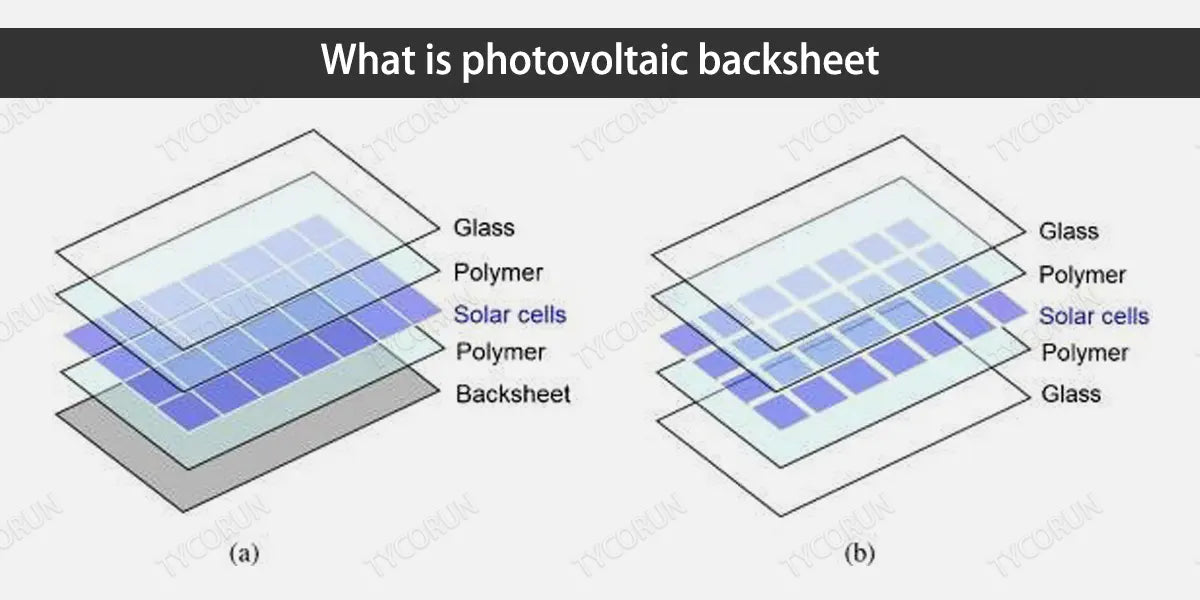
Photovoltaic backsheet is divided into inorganic backsheets, namely organic glass backsheets and polymer backsheets according to the materials they use. If the photovoltaic backsheet is also made of glass, it is a double glass module, otherwise it is a single glass module. One side of the component glass faces directly from the sun, and the back high efficiency solar panels are located on the back of the component.
At present, photovoltaic modules are mainly single glass modules, but the development trend is that the proportion of double glass modules will gradually increase, because double glass modules can generate electricity on both sides and improve power generation efficiency.
● Structure of photovoltaic backsheet
The photovoltaic backsheet is located in the outermost layer of the back of the photovoltaic module, in direct contact with the external environment over a large area. In order to adapt to a variety of climatic environments and service times, the photovoltaic backplane needs to meet a variety of performance requirements.
It is difficult for a single material to meet these performance requirements, so photovoltaic backsheet generally uses composite structures. Among them, PET film is used as a base film, fluorine film or other plastic film adhered to both sides of the base film by adhesives.
PET film has excellent insulation properties and mechanical properties, but poor weather resistance, fluororesin film includes polyvinylidene fluoride (PVF) film and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film. They have excellent insulation, weather resistance and barrier, and the main function of the adhesive is to bond and composite PET-based film with fluorine film and polyolefin film. According to the production process, the backplane is divided into composite type and coated type.
The fluorine material is compounded (generally pressed) on the PET film by the adhesive in the form of fluorine film, that is, the composite backplate, and its fluorine film is complete, so the overall performance is superior, but the cost is high.
In the form of fluororesin, it is directly coated on the PET base film through a special process, and the adhesive is mixed in fluororesin, which is a coated backsheet, which has slightly inferior performance to the composite backsheet, but has a price advantage.
● Classification of photovoltaic backsheet
Photovoltaic backsheet can be divided into double-sided fluorine film backsheets, single-sided fluorine film backsheets, and fluorine-free backsheets according to fluorine-containing conditions, which are suitable for different environments because of their different weather resistance and other characteristics.
In general, the degree of weather resistance to the environment is double-sided fluorine film backplate, single-sided fluorine film backplate, and fluorine-free backplate. Its price is generally reduced in turn.
Due to its superior weather resistance, the double-sided fluorine film composite backsheet can withstand harsh environments such as cold, high temperature, wind and sand, and rain. It is usually widely used in plateaus, deserts, Gobi and other regions.
Single-sided fluorine film composite backsheet is a cost-reducing product of double-sided fluorine film composite backsheet. Compared with the double-sided fluorine film composite backsheet, its inner layer has poor UV resistance and heat dissipation, and is mainly suitable for roofs and areas with mild ultraviolet rays.
2. The function of the photovoltaic backsheet
Photovoltaic backsheet is widely used in solar battery (photovoltaic) modules and are located on the back of solar panels. Protect solar modules from water vapour in outdoor environments, block oxygen and prevent module internal oxidation. They have reliable functions including:

- Insulation
- Water resistance
- Aging resistance
- High and low temperature resistance
- Corrosion resistance
It can reflect sunlight and improve the conversion efficiency of components. It has a high infrared reflectivity, which can reduce component temperature.
3. The layout status of the photovoltaic backsheet
The global photovoltaic industry chain is basically in China, and the same is true for photovoltaic backsheet. With the rapid rise of the top 10 photovoltaic battery companies in the world, China has gradually gained market share. In the early days, TPT and KPK backsheets were the mainstay, but the price of PVF and PVDF films was high.
In particular, PVF films are basically only produced by DuPont in the United States. Therefore, through research and development, Chinese companies replace fluorine film with fluorine-containing coatings and replace composite processes with coating processes. And the cost is greatly reduced under the premise of meeting the performance of photovoltaic modules.
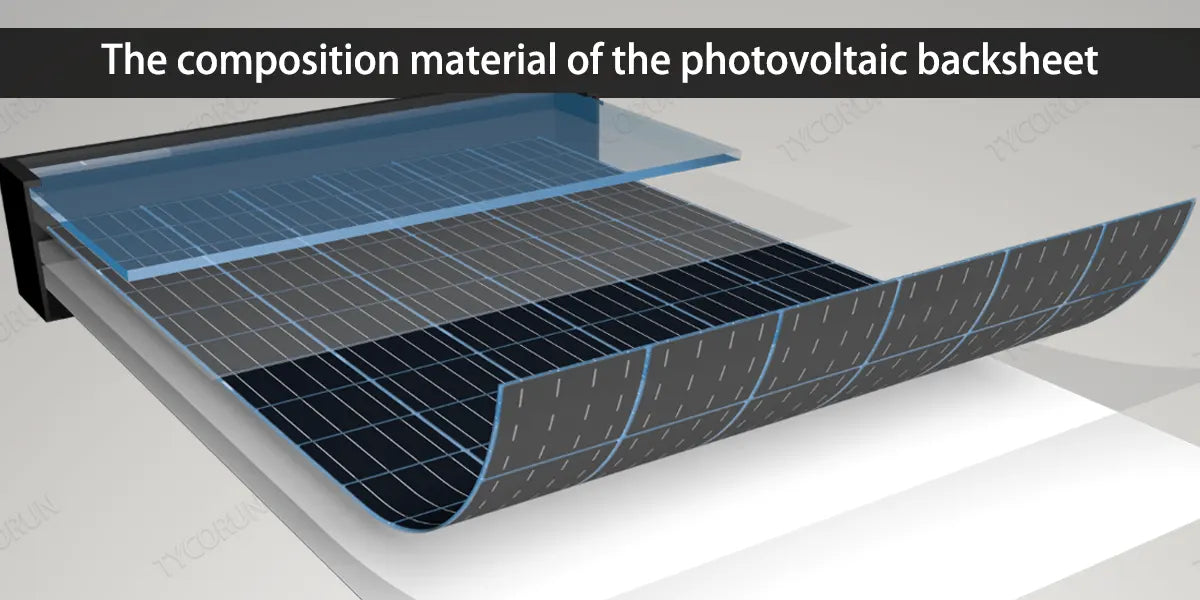
4. The composition material of the photovoltaic backsheet
● PET-based film
PET is a crystalline polymer. Long-term use can withstand high temperature up to 120 °C, short-term use can withstand 150 °C high temperature, -70 °C low temperature, and high and low temperature has little effect on its mechanical properties. Among them, the high-end PET film is mainly used for optical film and photovoltaic backsheet film, which has the following characteristics:
- Long equipment cycle
The output of the key base film production process is efficient, the delivery cycle is long, and the installation and commissioning time is also long.
- High technical requirement
Polymer material formulations are different, and material properties vary greatly. Even with the same recipe, process parameters change, and performance changes. These require long-term accumulation, and only advanced equipment is not enough, but also requires a large number of technicians with practical experience.
In order to adapt to the new photovoltaic backsheet structure, various substrate film companies are stepping up research and development of highly weather resistant transparent PET substrates.
● Fluorine membrane
After more than 30 years of practical application, it has proved that its structure and performance are stable, and it can meet the time requirements of components for more than 25 years. However, T-membranes are expensive, so the market size is decreasing, mainly for large-scale ground power stations.
To further reduce costs, each company has developed fluorine-containing coatings. Because fluoroplastics are not easy to decompose, incineration will produce toxic gases, so recycling photovoltaic backsheet is difficult.
● Adhesives
Technical barriers to the production of adhesives required for photovoltaic backsheet production are high. Due to the ability to control costs and different use scenarios, centralized large-scale ground photovoltaic power plants are the mainstay. The service life of 25 years is strictly required, so most of China's backsheets contain fluorine. In order to reduce costs, the production process is improved from composite fluorine film to coated with fluorine containing coatings.
5. The future development direction and prospect of photovoltaic backsheet
● Environmental protection
The main purpose of the large-scale use of new energy is to reduce emissions and protect the atmosphere. Therefore, the components used to manufacture photovoltaic modules should also be environmentally friendly. However, the fluorine film used in the photovoltaic backsheet is difficult to degrade, resulting in difficult recycling. Therefore, with the rapid development of photovoltaic power generation, the recycling of photovoltaic backsheet is a problem to be solved.
● Cost reduction
Cost reduction and efficiency improvements in all aspects of the photovoltaic industry chain are the main driving force for the development of photovoltaics, and fluorine membranes are neither environmentally friendly nor expensive. Therefore, the development of new materials to replace fluorine membranes is imminent.

● Development of photovoltaic backsheet for different usage scenarios
For example, the backplane used in the western desert area of China needs to have better heat dissipation, ultraviolet resistance, wind and sand wear resistance, and resistance to day and night temperature differences. The backplate applied on the east coast should have a lower water vapor transmission rate, better resistance to hydrolysis and resistance to salt spray.
● Suitable for the needs of bifacial power generation
Component bifacial power generation is the general trend, its proportion is getting higher and higher, and module manufacturers generally use glass backplanes. Although transparent backplates can replace glass backplates, transparent backplates have not been tested for a long time.
6. Conclusion
The internal driving force driving the PV backsheet industry is mainly performance and cost. From the performance point of view, the backplane of high demand components basically uses fluorine-containing materials to protect PET, and the difference is only that the fluorine materials used are different.
From the perspective of cost, the cost of coating is much lower than that of lamination. The ultimate trend of backsheets should be to find a material with better weather resistance to replace PET backsheets.
Related articles: Top 5 distributed photovoltaic companies, Top 5 perovskite solar cell companies, solar panel recycle