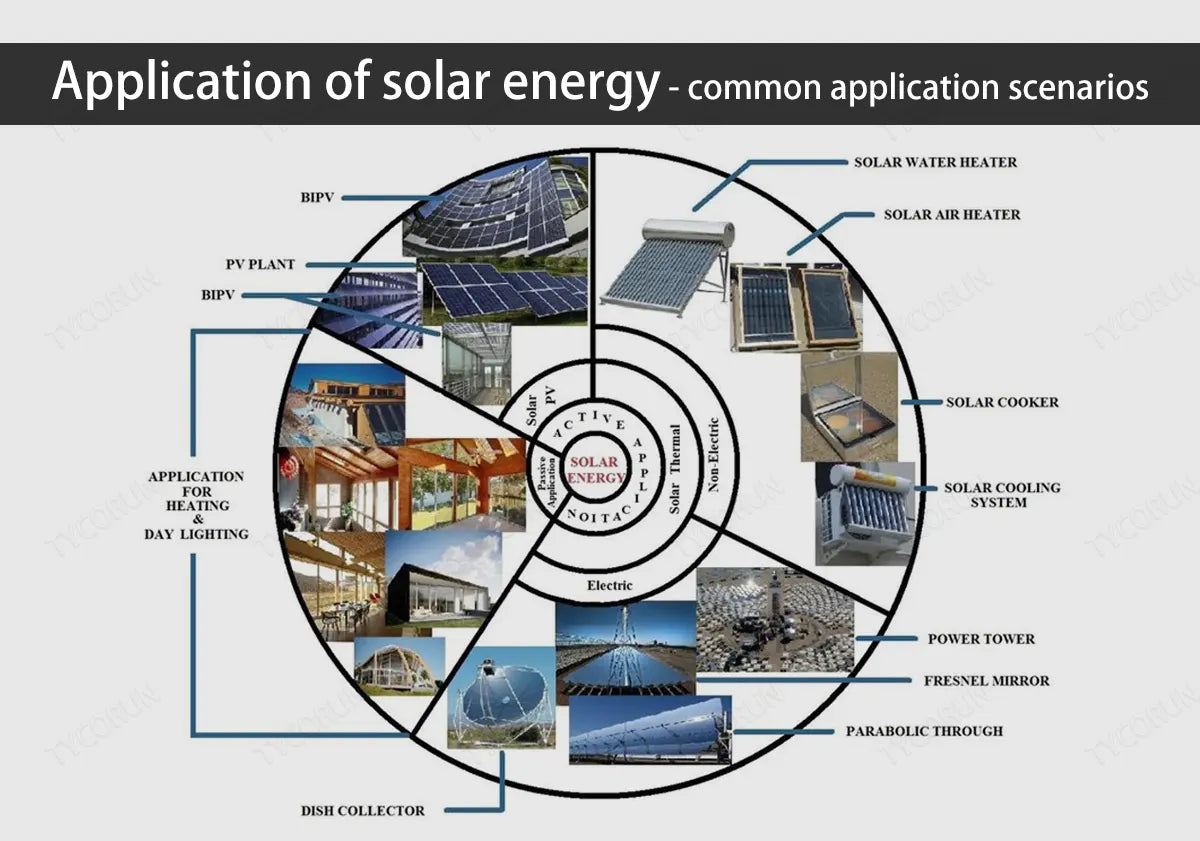
Solar technology is a technology that uses the sun's light and heat to provide us with electricity or heat. There are many types of solar energy technology, such as solar panels that can convert sunlight into electric current with solar inverters like 2000w inverter or 3000w inverter, solar water heaters that can convert solar heat into hot water, and solar batteries that can use sunlight to drive vehicles, etc.
The application of solar energy not only brings us convenience and savings, but also protects our environment and resources. This article will introduce you to some common scenarios of application of solar energy.
Main content:
1. Application of solar energy for residential uses
The application of solar energy in residential settings is growing in popularity, providing house owners with a sustainable and cost-effective solution. Key components for residential solar applications include solar panels for electricity generation, solar water heaters, solar appliances, lighting, and integration with smart home systems. Not only do these systems help reduce your carbon emission, they also increase energy independence and can significantly reduce your electricity bill.
① Household solar panels
Solar panels, or photovoltaic (PV) panels, convert sunlight into electricity and provide the primary energy source for a home. Typical specifications for residential solar panels include:
- Power output: Typically ranges from 250 to 400 watts per panel.
- Efficiency: The average efficiency is between 15% and 20%.
- Size and dimensions: Standard panel size is approximately 65 inches x 39 inches.
- Lifespan: Most solar panels come with a 25-year warranty, which indicates they have a long lifespan.
- Cost: Cost can vary by capacity, brand, and technology, but on average, a residential solar system costs between $10,000 and $20,000 to install after tax credits and incentives.

② Solar water heater
Solar water heater is an application of solar energy to heat water and then store the water in an insulated tank for use. Key aspects include:
- Type: The main types are active solar water heating system and passive solar water heating system.
- Capacity: Usually 100 to 300 liters.
- Cost: The initial installation cost may be higher than a traditional water heater, but the long-term savings in utility bills are substantial.
- Efficiency: These systems can provide approximately 50%-70% of a home's hot water needs, depending on climate.
③ Solar appliances and lighting
Advances in solar technology have led to the development of a variety of solar appliances and lighting solutions. Key aspects include:
- Type: Solar refrigerators, air conditioners and lights, etc.
- Advantages: Reduced electricity bills, low maintenance costs, and reduced dependence on the power grid.
- Efficiency and quality: Solar equipment continues to improve in efficiency and functionality, making it comparable to traditional equipment.
④ Integrate with smart home systems
Integrating home solar power system with smart home technology is a trend to enhance energy management and maximize efficiency.
- Automation: Smart thermostats and AI-based energy management systems optimize the application of solar energy.
- Monitoring: House owners can monitor real-time energy production and consumption, adjusting usage patterns to maximize energy savings.
- Cost and value: While integration with smart home systems may incur additional costs, the overall value it adds in terms of energy savings and efficient application of solar energy is tremendous.
2. Application of solar energy for commercial and industrial uses
The application of solar energy solutions in the commercial and industrial sectors are gaining attention for their long-term cost savings, sustainability benefits, and efficiency in meeting large-scale energy needs.
These industries process the application of solar energy in various forms, from large-scale solar power plants to specific applications such as manufacturing, building heating and agricultural use, each meeting unique energy needs through innovative solar technologies.
① Large solar power plant
Large-scale solar power plants play a vital role in generating electricity on a large scale. These factories typically cover large areas of land and are made up of thousands of solar panels.
- Capacity: Solar farms can range in size from a few megawatts (MW) to, in some cases, gigawatts (GW).
- Efficiency: As technology advances, the efficiency of large solar installations continues to increase, often exceeding 20%.
- Investment and return: The initial investment in setting up a solar farm can be substantial. However, over time, the return on investment, combined with various government incentives and the falling cost of solar technology, it will financially be feasible.
- Lifespan and maintenance: Solar plants typically have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years and require minimal maintenance compared to traditional power plants.

② Solar energy in the manufacturing process
Manufacturing industries are increasingly turning to solar power to power their operations, from running machinery to lighting and heating.
- Applications: Solar energy can be used in processes such as assembly line operations, machine tools, and cooling systems.
- Cost-effectiveness: While the upfront cost of solar installation can be high, reduced utility bills and potential tax benefits make solar a cost-effective solution for manufacturers.
- Sustainable development: The application of solar energy can help manufacturers reduce their carbon footprint and achieve sustainability goals.
③ Solar heating for commercial buildings
Solar heating systems are becoming a popular choice for heating commercial buildings, from offices to warehouses and retail spaces.
- Type: Common types include solar hot water systems and solar air heaters.
- Cost and efficiency: Solar heating systems are more cost-effective than traditional heating methods. They can significantly reduce utility bills, especially in areas with higher sunlight levels.
- Integration: These systems often integrate seamlessly with existing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, improving overall energy efficiency.
④ Agriculture and plantation equipment
The agricultural sector is using solar energy to power various operations and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices.
- Applications: Include powering irrigation systems, heating greenhouses and running agricultural machinery.
- Benefits: Solar energy can help farmers reduce energy costs, withstand energy price fluctuations, and even serve as an additional source of income if excess power is sold back to the grid.
- Systems and specifications: Photovoltaic (PV) systems used in agriculture vary depending on the application, but generally they are designed to be rugged and require minimal maintenance, making them suitable for harsh agricultural environments.

3. Application of solar energy for transport and mobility
Driven by the desire to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and achieve energy independence, the transportation industry is increasingly turning to solar energy. This shift involves integrating solar technology into all forms of transportation and supporting infrastructure, including solar electric vehicles (EVs), charging stations, public transportation systems, and even extending into the maritime and aviation industries.
① Solar electric vehicle (EV)
Solar-powered electric vehicles are at the forefront of green transportation innovation. The vehicles either have integrated solar panels or are charged using solar charging stations.
- Integration and efficiency: Most solar electric vehicles have integrated panels on roofs and other surfaces. These panels often supplement the vehicle's main power supply, increasing the range and efficiency.
- Power output: Although limited in size, the solar panels on these vehicles can produce enough electricity to significantly increase the car's range - typically about 30 to 60 miles on a sunny day.
- Cost and market availability: The cost of solar electric vehicles varies widely depending on the model and solar technology. They are currently more expensive than traditional electric cars, but offer the advantages of lower charging costs and reduced environmental impact.
② Electric vehicle solar charging station
Solar charging stations provide renewable and often off-grid electricity to electric vehicles, further reducing the carbon footprint of electric vehicle transportation.
- Capacity and speed: These charging stations range from high-capacity fast charging stations that can fully charge a vehicle in a few hours, to small portable chargers for emergency charging.
- Installation and cost: Installation of solar charging stations involves a significant investment, but this can be offset by government incentives and lower operating costs over time.
③ Public transportation solutions
Public transportation systems also process the application of solar energy to reduce operating costs and increase sustainability.
- Application: In terms of public transportation solutions, application of solar energy mainly include solar buses, trains and trams. Many bus stations and warehouses use solar panels to generate electricity for lighting, ticketing systems and other power needs.
- Benefits and efficiency: These applications not only reduce fuel costs but also help clean the air and reduce urban noise pollution.
④ Navigation and aviation industry
The application of solar energy is starting to make inroads into shipping and aviation, although progress has been slow due to technical and practical challenges.
- Maritime applications: Solar-powered ships typically use off grid solar batteries to power onboard systems and, in some cases, provide propulsion.
- Aviation projects: Although still in their early stages, solar aviation projects such as Solar Impulse have shown the potential of solar power in air travel, although currently limited to small aircraft and experimental designs.

4. Application of solar energy for public infrastructure and community projects
The application of solar energy is widely used in public infrastructure and community projects due to its versatility and scalability. These applications not only provide sustainable, cost-effective energy solutions, but also enhance the aesthetic and functional value of public spaces.
Projects such as solar street lighting, solar public spaces and community solar initiatives reflect how solar technology can meet wider community needs beyond individual homes or businesses.
① Solar street lights
Solar street lights are a prominent and widely used project of solar energy in public infrastructure. The lights use solar panels mounted on top of the poles to charge during the day and illuminate the streets at night.
- Efficiency and maintenance: Solar street lights using LED are highly efficient and require minimal maintenance. They are a reliable form of lighting, especially in areas without grid access.
- Installation cost and lifespan: Solar street light installation may cost more to install than traditional street lights, but they can lead to long-term savings through reduced energy bills and lower maintenance costs. The service life of solar street lights is usually very long, usually more than 20 years.
② Solar-powered public spaces and parks
Parks, gardens and other public spaces are increasingly using solar energy to power lights, fountains, charging stations and even Wi-Fi routers.
- Benefits: Not only does this reduce the carbon footprint of public spaces, it also improves safety and accessibility after dark.
- Community engagement: These installations can increase public awareness and acceptance of solar technology as a viable and practical energy source.
③ Community solar projects
Community solar projects allow multiple individuals or entities to share the benefits of a single solar project, which is typically set up in a shared community space.
- Accessibility and cost savings: These projects are particularly beneficial for people who are unable to install solar panels on their own homes due to cost, location, or lack of sunlight. Participants can save on electricity bills while supporting renewable energy.
- Structure and scalability: Community solar projects can vary in size and structure and are often tailored to meet the specific needs and goals of the communities they serve.
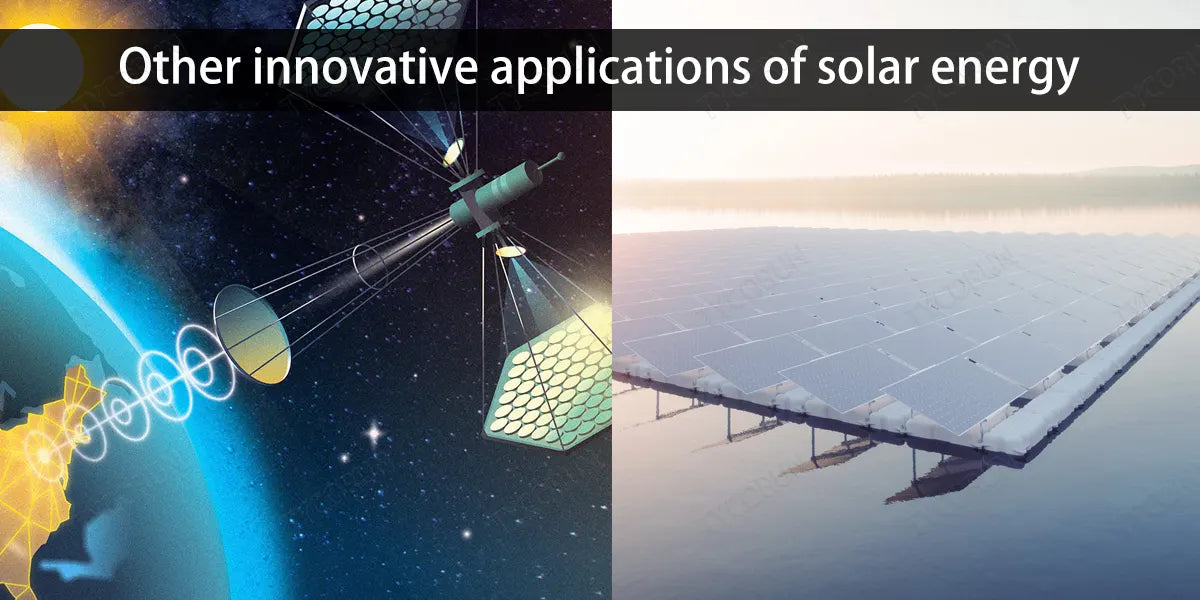
5. Other innovative applications of solar energy
The solar field is not only expanding, but also innovating, pushing the boundaries of technology and practicality. From powering space missions to integrating into building designs, solar energy is proving its versatility and ability to innovate.
These developments mark a major shift in the way we view and use solar technology, moving beyond traditional panels and toward more creative and impactful applications.
① Space exploration
Solar energy plays a vital role in space exploration, providing reliable and efficient power for spacecraft, satellites and even extraterrestrial bases.
- Efficiency and reliability: In space, sunlight is more intense and uninterrupted, and solar panels operate more efficiently compared to Earth. These panels power countless space missions, providing reliable power far from Earth.
- Developments and challenges: As missions aim further into space, the need for more advanced solar technology becomes apparent. Challenges include improving the durability of solar panels in harsh space conditions and increasing their energy-to-weight ratio.
② Floating solar plants
Floating solar power plants, or floating photovoltaics are an innovative use of solar panels installed on floating structures on bodies of water such as lakes, reservoirs and ponds. These farms solve land-use issues and allow for large-scale solar installation without taking up valuable land space.
The water underneath helps cool the panels, increasing their efficiency and reducing evaporation from the water body. While initial installation costs may be higher than for land-based solar farms, the benefits of reduced land use and increased efficiency can offset these costs.
③ Building integrated photovoltaic (BIPV)
BIPV technology integrates photovoltaic materials into building structures, such as facades, roofs or windows.
- Aesthetics and functionality: BIPV systems can not only generate electricity, but also add architectural appearance to buildings. They replace traditional building materials, thereby reducing overall material costs.
- Energy efficiency: BIPV can significantly reduce a building’s carbon footprint by meeting a portion of the building’s electricity needs. Effects vary depending on factors such as building orientation, climate and BIPV design.
Related posts: global top 10 best solar inverter brands, working principle of inverter, car inverter near me